Credentials & Security
Credentials allow Yattee Server to access content that requires authentication -- age-restricted videos, premium content, region-locked material, and password-protected streams. Currently, Yattee Server supports authentication via cookie files in Netscape format.
How Credentials Work
When Yattee Server extracts video information or streams content through yt-dlp, it passes any configured credentials for the relevant site as command-line flags. This allows yt-dlp to authenticate on your behalf without exposing credentials to clients.
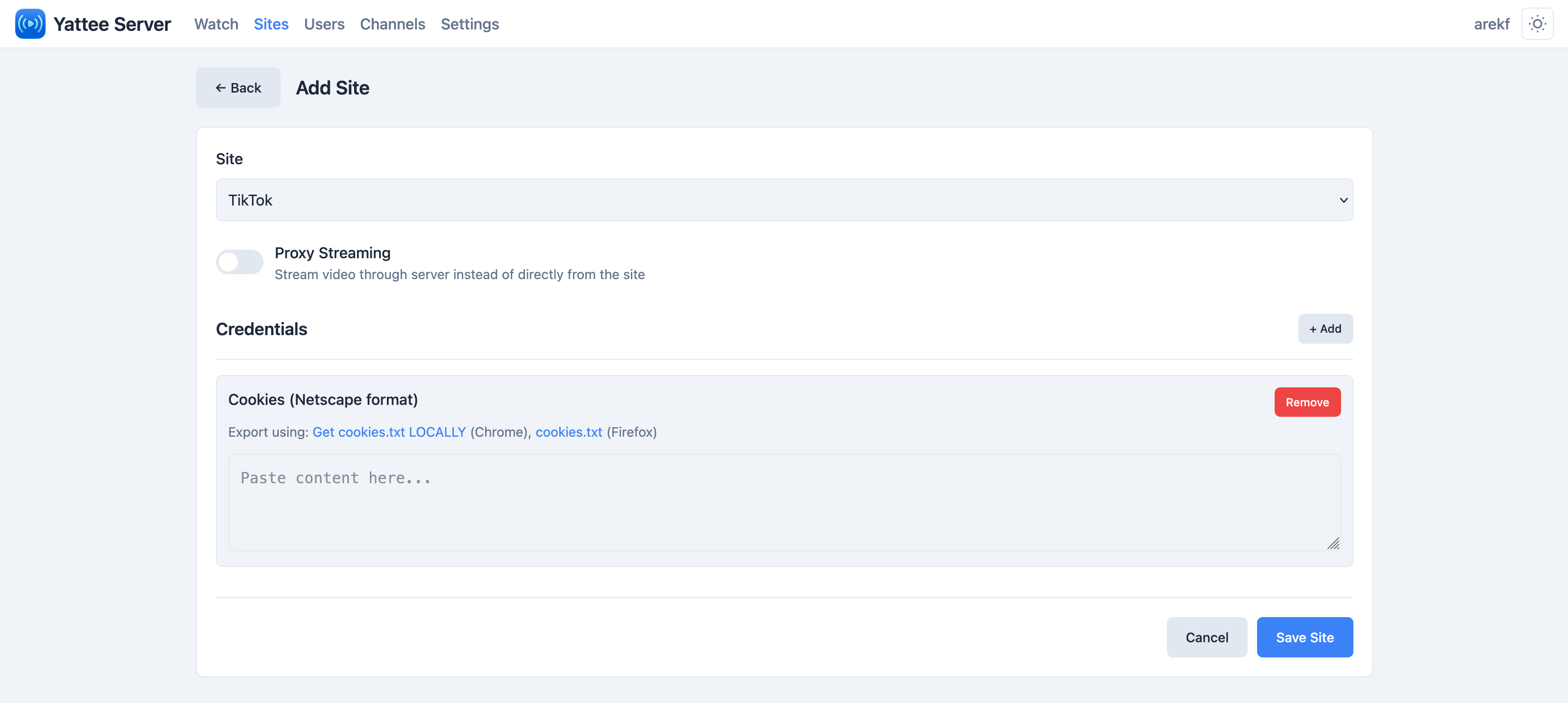
Cookie File Credential
The cookies_file credential type maps to the yt-dlp --cookies flag. It accepts cookie file contents in Netscape format, which is the standard format used by browser cookie-export extensions.
The most reliable method for YouTube authentication is exporting cookies from your browser using an extension like "Get cookies.txt LOCALLY", then pasting the contents into the credential value field.
Setting Up Credentials
YouTube with Cookies
- Install a cookie export extension in your browser (e.g., "Get cookies.txt LOCALLY" for Chrome/Firefox).
- Log into YouTube in your browser.
- Export cookies for
youtube.comin Netscape format. - In the Yattee Server admin panel, navigate to the YouTube site configuration.
- Add a new credential of type cookies_file.
- Paste the entire cookie file contents into the value field.
- Save and use the Test button to verify the credentials work.
Testing Credentials
Each site in the admin panel has a Test button that attempts to extract a video URL using the configured credentials. This is the quickest way to verify that your credentials are working correctly. If the test fails, check the server logs for detailed error messages from yt-dlp.
Encryption
Sensitive credential values are automatically encrypted at rest using Fernet symmetric encryption (AES-128-CBC with HMAC-SHA256 authentication).
The cookies_file credential type is encrypted before being stored in the database.
Encryption Key
The encryption key is auto-generated on first server startup and stored at:
{DATA_DIR}/.encryption_key
The key file is created with restricted permissions (0600 -- owner read/write only).
You can also provide your own encryption key via the CREDENTIALS_ENCRYPTION_KEY environment variable. If set, this takes precedence over the file.
If the .encryption_key file is deleted or corrupted and you have not backed it up or set CREDENTIALS_ENCRYPTION_KEY, all encrypted credentials become permanently unrecoverable. You will need to re-enter every credential.
Always include the DATA_DIR directory in your backup strategy.
API Security
Credential values are never exposed in API responses. When querying credentials through the API, the server only returns:
{
"type": "cookies_file",
"has_value": true
}
The actual credential content is never transmitted back to any client.
Cookie File Handling
When yt-dlp needs to use a cookies_file credential during extraction:
- The decrypted cookie contents are written to a temporary file with
0600permissions. - The temp file path is passed to yt-dlp via the
--cookiesflag. - After yt-dlp completes (success or failure), the temp file is immediately deleted.
This ensures cookie data exists on disk only for the duration of the extraction.